03 路由和负载均衡
让我们放大 Traefik 的体系结构,并讨论支持创建路由的组件。
首先,在启动 Traefik 时,定义入口点(在它们最基本的形式中,它们是端口号)。 然后,连接到这些入口点,路由器分析传入的请求,看它们是否匹配一组规则。 如果匹配到规则,路由器可能会使用中间件转换请求,然后再将它们转发到处理请求的服务。
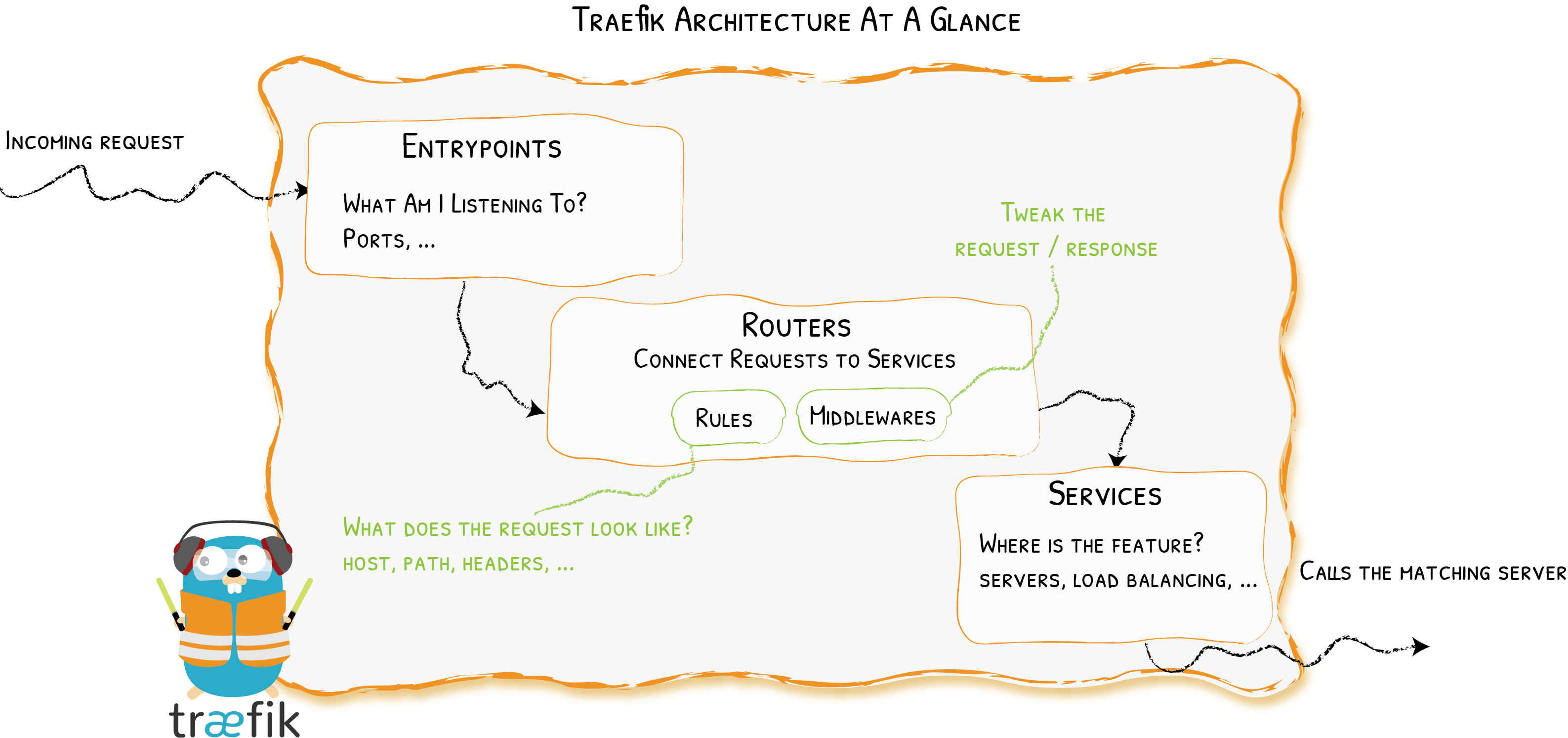
0.1. 明确职责
- 提供者(Providers)发现基础设施上的服务(他们的 IP,健康,...)
- 入口点(Entrypoints)监听传入通信(端口,...)
- 路由器(Routers)分析请求(主机,路径,请求头,SSL,...)
- 服务(Services)将请求转发给服务(负载平衡,...)
- 中间件(Middleware)可以更新请求或根据请求做出决定(身份验证,速率限制,请求头,...)
0.2. 文件提供者示例
下面是一个文件提供者的完整配置文件的例子,这个文件提供者可以将 http://domain/whoami/ 请求转发到 http://private/whoami-service/ 上可访问的服务。 在此过程中,Traefik 将确保对用户进行身份验证(使用 BasicAuth 中间件)。
静态配置:
entryPoints:
web:
# Listen on port 8081 for incoming requests
address: :8081
providers:
# Enable the file provider to define routers / middlewares / services in a file
file:
filename: dynamic_conf.yml动态配置:
# http routing section
http:
routers:
# Define a connection between requests and services
to-whoami:
rule: "Host(`domain`) && PathPrefix(`/whoami/`)"
# If the rule matches, applies the middleware
middlewares:
- test-user
# If the rule matches, forward to the whoami service (declared below)
service: whoami
middlewares:
# Define an authentication mechanism
test-user:
basicAuth:
users:
- test:$apr1$H6uskkkW$IgXLP6ewTrSuBkTrqE8wj/
services:
# Define how to reach an existing service on our infrastructure
whoami:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: http://private/whoami-service在本例中,我们使用文件提供者。 即使它是配置 Traefik 的最不神奇的方法之一,它也明确地描述了每一个可用的概念。
0.2.1. HTTP / TCP
在这个例子中,我们只为 http 请求定义了路由规则。 Traefik 还支持 TCP 请求。 要添加 TCP 路由器和 TCP 服务,请在 TCP 部分中声明它们,如下所示。
静态配置:
entryPoints:
web:
# Listen on port 8081 for incoming requests
address: :8081
providers:
# Enable the file provider to define routers / middlewares / services in a file
file:
filename: dynamic_conf.yml动态配置:
# http routing section
http:
routers:
# Define a connection between requests and services
to-whoami:
rule: Host(`domain`) && PathPrefix(`/whoami/`)
# If the rule matches, applies the middleware
middlewares:
- test-user
# If the rule matches, forward to the whoami service (declared below)
service: whoami
middlewares:
# Define an authentication mechanism
test-user:
basicAuth:
users:
- test:$apr1$H6uskkkW$IgXLP6ewTrSuBkTrqE8wj/
services:
# Define how to reach an existing service on our infrastructure
whoami:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: http://private/whoami-service
tcp:
routers:
to-whoami-tcp:
service: whoami-tcp
rule: HostSNI(`whoami-tcp.traefik.io`)
services:
whoami-tcp:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- address: xx.xx.xx.xx:xx0.3. 传输配置
客户端和 Traefik 之间的连接,以及 Traefik 和后端服务之间的连接,大部分都是通过入口点和路由器配置的。 此外,还有一些参数专门用于在全局范围内配置 Traefik 和后端之间的连接。 这是通过配置serversTransport 完成的,它提供了以下选项:
0.3.1. insecureSkipVerify
禁用 SSL 证书验证。可选,默认为false
## Static configuration
serversTransport:
insecureSkipVerify: true0.3.2. rootCAs
当使用自签名 TLS 证书时,rootCAs就是证书列表(作为文件路径或数据字节)将会被设置为根证书授权。可选
## Static configuration
serversTransport:yaml
rootCAs:
- foo.crt
- bar.crt0.3.3. maxIdleConnsPerHost
可选,默认为2,如果非零,maxidlecon/nsperhost控制每个主机保持的最大空闲(keep-alive)连接。
## Static configuration
serversTransport:
maxIdleConnsPerHost: 70.3.4. forwardingTimeouts
Forwardingtimeouts 与向后端服务转发请求时的大量超时有关。
0.3.4.1. forwardingTimeouts.dialTimeout`
可选。默认为30s
Dialtimeout 是建立到后端服务的连接所允许的最大持续时间。 零意味着没有超时。
## Static configuration
serversTransport:
forwardingTimeouts:
dialTimeout: 1s0.3.4.2. forwardingTimeouts.idleConnTimeout`
可选。默认90s
Idlekonntimeout,是空闲(keep-alive)连接在关闭自身之前保持空闲的最大时间量。 零意味着没有限制。
## Static configuration
serversTransport:
forwardingTimeouts:
idleConnTimeout: 1s